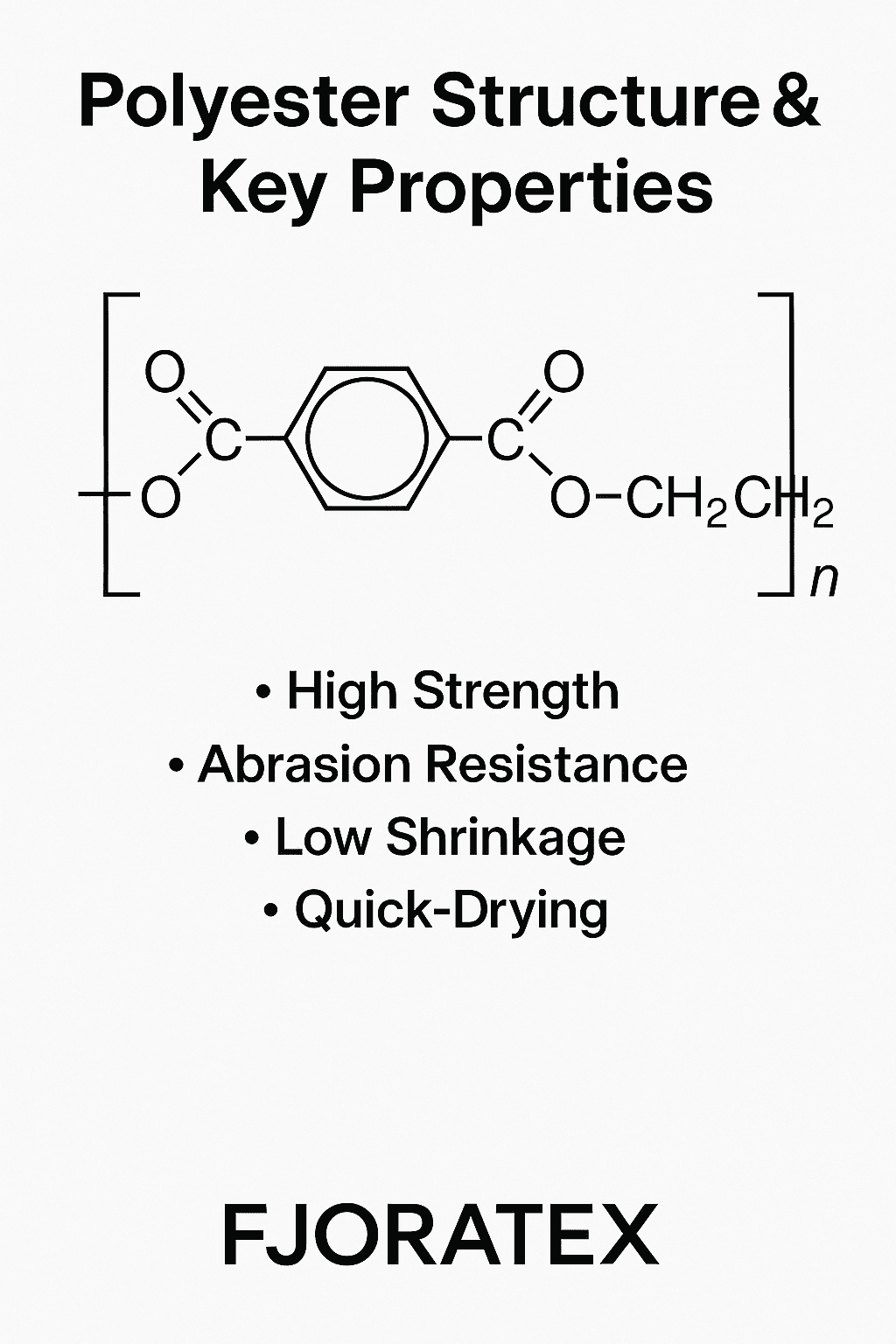
Polyester is one of the most widely used synthetic fibers in the world, playing a vital role in apparel, home textiles, functional fabrics, and industrial materials. Its broad application is not simply due to affordability or availability — the real strength of polyester lies in its molecular structure and material properties, which provide a balance of durability, functionality, and versatility that few materials can match.
While many people associate polyester with being “common” or “inexpensive,” the fiber’s advantages go far beyond surface impressions. Understanding the technical foundation of polyester helps reveal why it remains a cornerstone of modern textiles.
High Strength and Excellent Durability
At a structural level, polyester is composed of highly ordered linear polymer chains formed by aromatic rings and ester linkages. This gives the fiber outstanding mechanical strength, high tensile resistance, and impressive abrasion durability. Polyester fabrics perform exceptionally well in areas requiring strength and long-lasting wear, such as outerwear, backpacks, and activewear. The fiber’s inherent thermal stability also makes it suitable for diverse finishing and functional processing.
Dimensional Stability and Resistance to Shrinkage
Thanks to polyester’s high crystallinity and rigid molecular structure, fabrics made from this fiber resist deformation under heat and moisture. This translates to garments that maintain their shape and fit, ideal for technical outerwear and long-term performance apparel. Additionally, polyester fabrics are known for being easy to care for, with excellent resistance to shrinking and wrinkling, even after repeated washing.
Low Moisture Absorption and Quick-Drying Performance
Polyester’s molecular structure lacks hydrophilic groups, resulting in a low moisture absorption rate, typically below 1%. As a result, polyester fabrics offer fast-drying performance, making them ideal for sportswear, outdoor gear, and garments used in humid environments. The fabrics stay lightweight, dry quickly, and maintain wearer comfort, especially during high-intensity or demanding activities.
Thermoplasticity and Design Flexibility
Polyester’s strong thermoplastic properties allow for flexible design and diverse functionality. Fiber cross-sections can be engineered to create unique textures, special luster, or even unconventional profiles. Through advanced processing, polyester fabrics can incorporate added features such as water resistance, breathability, far-infrared insulation, and antibacterial performance. Polyester also blends easily with other fibers to optimize overall functionality.
Sustainable Development and Eco-Friendly Upgrades
Traditional polyester is primarily derived from petrochemical resources, but the industry is rapidly evolving toward more sustainable alternatives. Recycled polyester (rPET) and bio-based innovations are key drivers of this transformation.
A representative example is FJORATEX’s TIDEA® functional fiber series. TIDEA® fibers retain the core performance advantages of conventional polyester while integrating marine-sourced biological materials and recycled content, significantly reducing dependency on fossil-based resources.
At the same time, TIDEA® fibers incorporate advanced functionalities directly at the fiber level, including far-infrared thermal insulation, antibacterial protection, and enhanced durability. This approach delivers both technical performance and environmental responsibility, offering next-generation material solutions for consumers seeking comfort, functionality, and a reduced environmental footprint.